Follow These Simple Guidelines to Select the Right Seafood
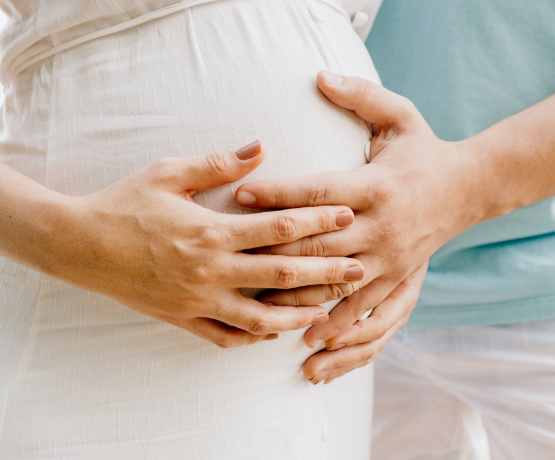
It’s no secret that seafood is good for your heart and brain, but you’ve probably also heard that some people should avoid certain types of fish when pregnant (or trying to get pregnant).
This is true. If you’re allergic to seafood, you should avoid it altogether. If you’re at higher risk for foodborne illness, you should avoid certain types of seafood. However, on the whole, most people who want to get pregnant or who are pregnant should increase their seafood intake. Seafood nutrition during pregnancy can be confusing! If you’re not allergic to it and you have questions about it, this post is for you.
I’m going to cut through the confusion and tell you about some of the nutrients found in seafood (including the famous omega-3 fatty acids), who should avoid which types of seafood (hint: not everyone), and let you in on some pro tips on selecting the healthiest seafood. Let’s begin by summarizing the impressive health benefits of eating seafood.
Health benefits of eating seafood before conception and while pregnant
Seafood contains nutrients for good health, including healthy fats, lean protein, vitamins, and minerals. It also contains omega-3s (more on these in the next section) which support the development of your baby’s brain and eyes, is associated with reduced allergies/asthma in children, and contributes to both egg and sperm health.
Eating seafood during pregnancy may also help to reduce the risk of certain complications, such as preterm birth and low birth weight. Studies have also shown that women who consume higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids during pregnancy have babies with higher cognitive development scores.
Healthy nutrients in fish for pregnancy
Seafood is lower in saturated fat than red meat. There are two main omega-3 fatty acids in seafood: EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). Seafood is the richest food source of EPA and DHA, but you can also supplement it. Click here to view our recommendation for a combined EPA/DHA supplement.
DHA is particularly good for your brain because it helps to keep it functioning efficiently. Your brain and nerves are partly made from fat, and they have a special preference for DHA. DHA deficiency is linked to serious cognitive problems, including Alzheimer’s disease. Consuming enough DHA regularly over the long-term is linked to improved ability to learn, improved memory, and a lower risk of cognitive decline.
You can also get DHA from algae and supplements. Regarding omega-3 supplements, recent studies show that supplementing with omega-3 fatty acids may not have the same positive impacts as eating the food itself. Eating seafood as part of a healthy dietary pattern seems to have the most health benefits, however if you don’t eat seafood, you may get some heart benefits from taking a fish oil supplement.
Seafood is also an excellent source of protein and contains essential minerals like vitamin B12, iodine, iron, selenium, and zinc. It is also one of the only foods with naturally occurring vitamin D.
If you cannot eat fish then you can also get essential fatty acids like avocados, extra virgin olive oil, seed butters, and nut butters. Click here to read more about our take on prenatal nutrition, including omega-3s.